Preparing for Implementation: A Practical Compliance Roadmap
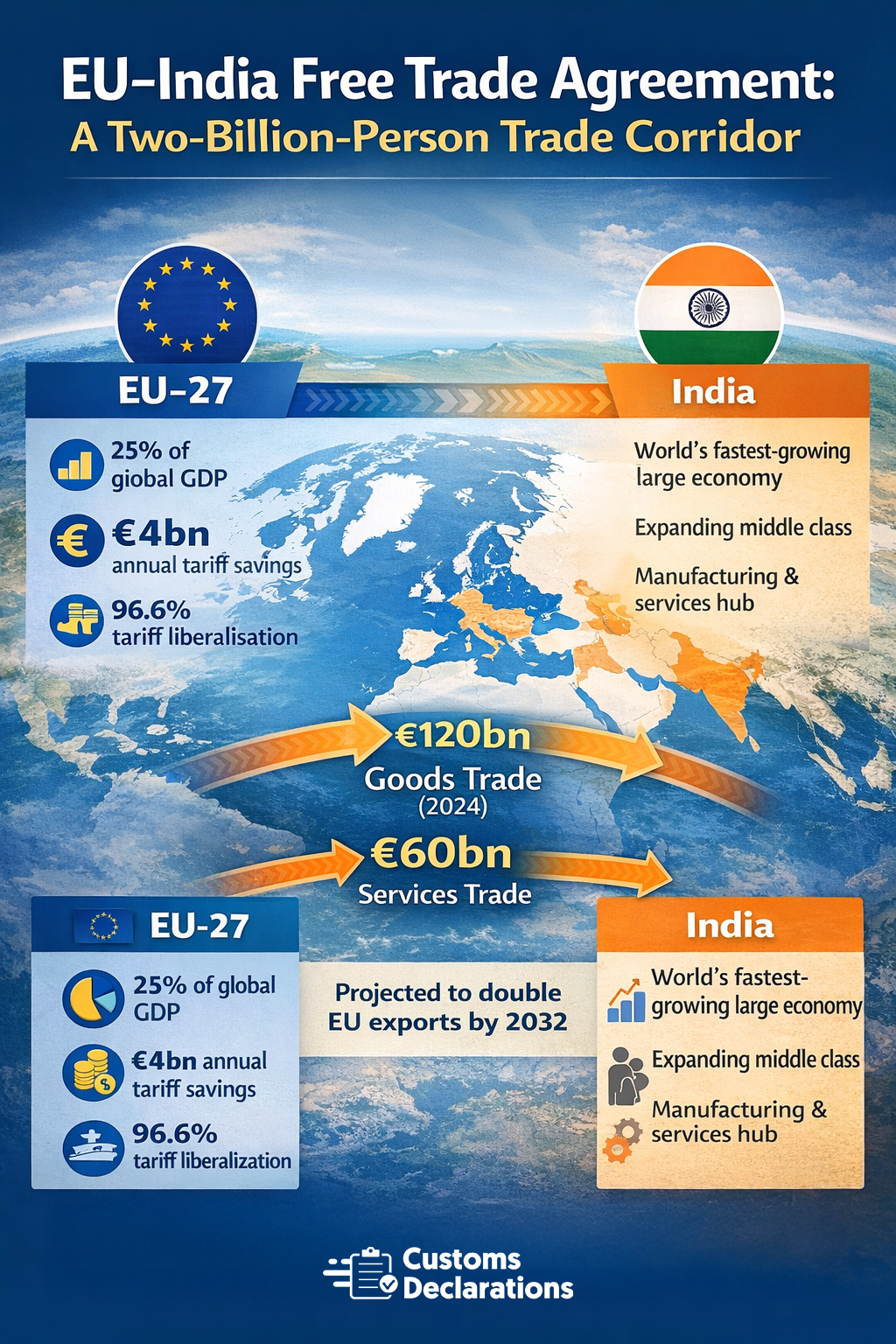
Businesses seeking to capitalize on the EU-India agreement should begin preparation immediately, even before formal signature and ratification. The following roadmap outlines key steps for customs, trade, and supply chain professionals.
First, conduct a comprehensive product portfolio review to identify goods currently exported to or imported from India, their tariff classifications, current duty rates, and projected preferential rates under the agreement. This analysis should prioritize high-volume or high-value product lines where tariff savings will be most significant. Second, map existing supply chains to assess origin eligibility under the agreement’s rules. For complex manufactured goods, this requires tracing inputs, production processes, and assembly locations to determine whether products will qualify as EU or Indian originating. Third, establish or strengthen supplier certification programs to obtain reliable origin declarations from vendors. Many businesses underestimate the time required to train suppliers, negotiate contractual origin clauses, and verify certification accuracy, making early engagement critical.
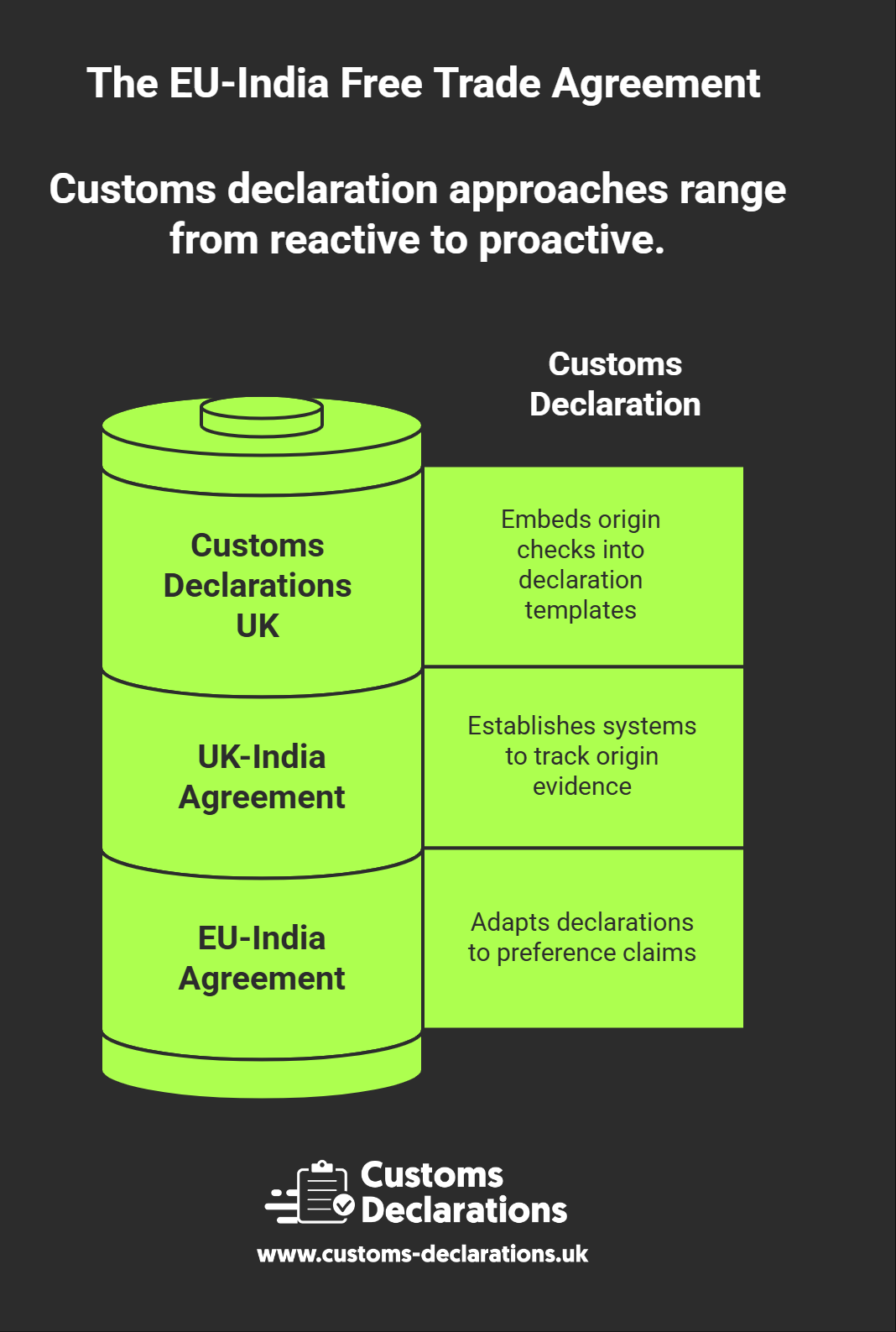
Fourth, update customs systems and declaration templates to accommodate preference claims, including fields for preference codes, origin statements, and quota references. Platforms such as Customs Declarations UK allow declarants to pre-configure preference logic, validation rules, and supporting documentation requirements so that preference claims are processed consistently and compliantly from the first shipment. Fifth, train internal teams on the agreement’s provisions, rules of origin requirements, and documentation standards. Cross-functional training should include procurement, logistics, finance, and legal teams to ensure that origin compliance is embedded across business processes, not treated as an isolated customs function.
Sixth, establish monitoring and audit protocols to verify ongoing compliance. Preference claims are subject to post-clearance verification by customs authorities, and businesses must be prepared to produce origin evidence, cost records, and production documentation on demand. Regular internal audits help identify and correct errors before they escalate into enforcement actions. Finally, engage with industry associations, legal advisors, and customs authorities to stay informed of implementation timelines, interpretive guidance, and any transitional measures that may affect initial preference claims.