Introduction: From Linear Chains to Learning Networks
For decades, supply chains have behaved like long, linear conveyor belts: plan, source, make, move, deliver. In a world of volatile demand, climate disruption, port congestion, and regulatory churn, that model no longer holds. The supply chain of the future looks less like a line and more like a responsive, learning network—sensing risk early, reasoning over billions of data points, and adjusting execution in real time. Artificial intelligence (AI) is the catalyst for this transformation. It augments human judgement with pattern recognition at scale, enables automation beyond routine tasks, and unlocks predictive and prescriptive decisions that were previously impractical.
This article maps how AI is reshaping end-to-end operations—from forecasting and production planning to transport, warehousing, and the border. It also explains what foundations you need (data, governance, skills) and answers the questions buyers, planners, logistics managers, and compliance teams are asking as they evaluate investments.
Why AI is the backbone of tomorrow’s supply chains
AI’s value is not just speed; it is the ability to connect dots people cannot see in time. Modern supply chains generate torrents of data from ERPs, telematics, port community systems, IoT sensors, weather feeds, social signals, and financial markets. AI transforms this noise into timely alerts and ranked options.
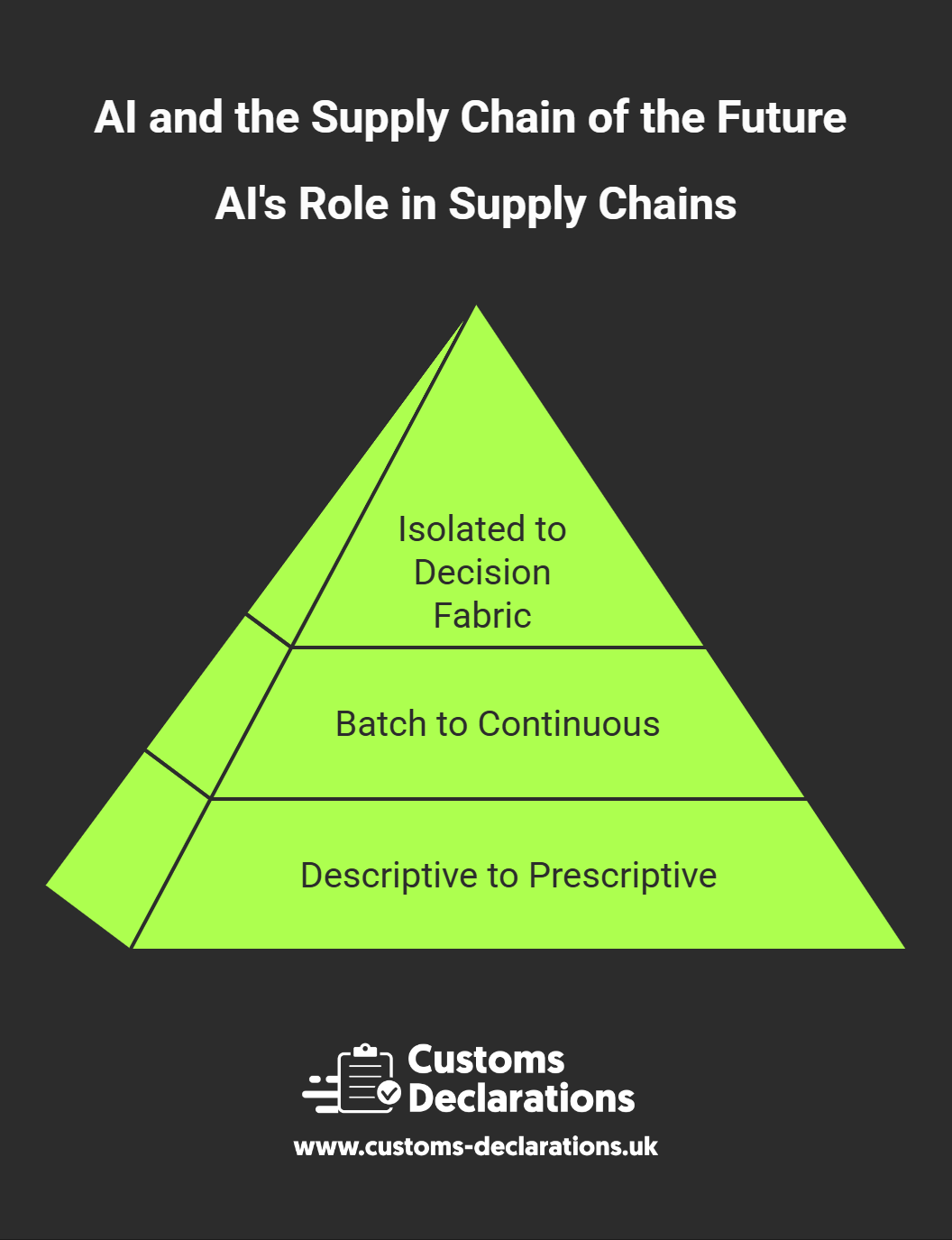
From descriptive to prescriptive. Traditional dashboards describe what happened. Machine-learning models forecast what is likely to happen (predictive), and optimisation engines recommend what to do next (prescriptive): resequence orders, shift production, re-route a sailing, or change a carrier mix to protect service level at the lowest total landed cost.
From batch planning to continuous orchestration. Classic S&OP cycles are monthly or weekly; AI makes micro-corrections hourly. Think of a living plan that adapts when a supplier misses a milestone, a motorway closes, or a heatwave narrows cold-chain capacity.
From isolated tools to decision fabric. The future is not one “AI app” but a fabric that connects demand, supply, logistics, and finance decisions. A forecast change instantly recalibrates warehouse labour plans, fleet dispatch, and cash-flow impact—without waiting for a meeting.
Demand sensing, planning, and inventory orchestration
Forecast accuracy underpins everything downstream. AI improves both signal quality and model responsiveness.
Demand sensing. Models ingest POS, web traffic, promotion calendars, weather, events, and competitive signals to detect early demand shifts. Short-term sensing feeds daily replenishment and allocation, while long-horizon models guide capacity and sourcing.
Inventory placement. AI evaluates channel elasticity, lead-time variability, and service goals to position buffer stock where it actually protects revenue. Instead of blanket safety-stock rules, you get SKU-channel-location policies tuned to volatility and margin.
Production scheduling. Reinforcement learning can optimise changeovers, energy pricing windows, and maintenance slots. Over time, the model learns the true penalty of late orders or overtime by observing outcomes, not just rules.
Logistics execution that adjusts itself in real time
AI’s impact is especially visible in transport, where small gains compound across thousands of moves.
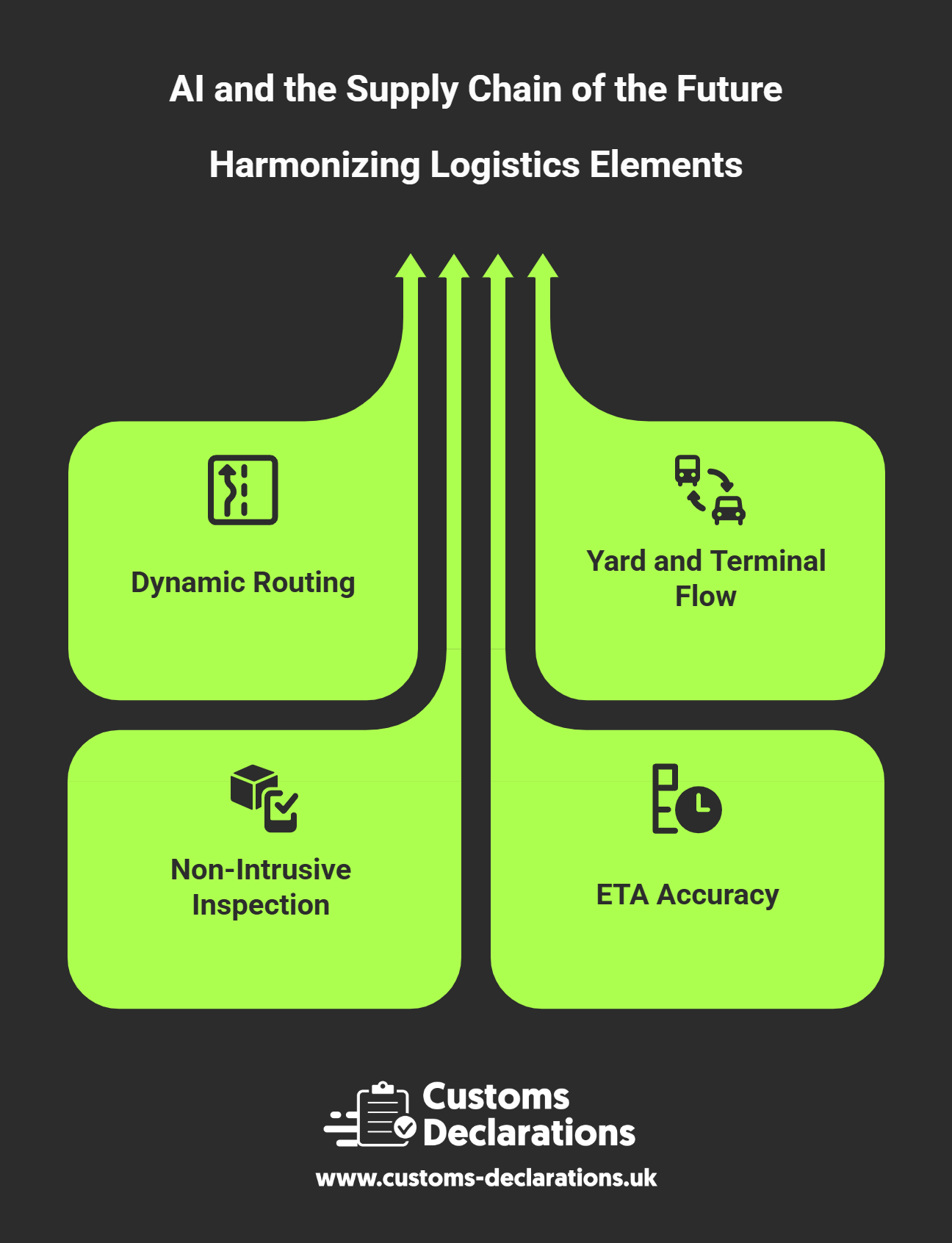
Dynamic routing and dispatch. Route engines continuously re-solve as traffic, weather, and delivery windows change. They weight emissions, tolls, driver hours, and vehicle constraints alongside speed. The result is fewer empty miles, more on-time stops, and lower cost per drop—without expecting drivers to improvise under pressure.
Yard and terminal flow. Computer vision tracks gate queues, dock utilisation, and equipment cycles, predicting bottlenecks before they form. When a surge hits, the system resequences slot bookings and dispatches additional shunt vehicles, preventing gridlock and detention.
Non-intrusive inspection and security. AI analysis of X-ray/CT images triages high-risk loads for manual inspection and clears low-risk cargo faster. That improves both compliance and velocity—vital for perishable and high-value goods.
ETA accuracy as a service promise. Models blend AIS vessel positions, rail performance, historical lane reliability, and real-time road conditions to provide credible ETAs. Customers receive fewer “surprise delays,” and planners can resequence work with confidence.
Warehousing: from fixed layouts to adaptive, human-in-the-loop automation
Inside the four walls, AI coordinates people, robots, inventory, and energy.
Work allocation and slotting. Algorithms assign tasks to pickers and AMRs (autonomous mobile robots) based on travel distance, congestion, and ergonomics, then dynamically re-slot fast movers to reduce footsteps and recharge cycles.
Computer vision QA. Cameras verify counts, label legibility, and damage at receiving and packing. The system flags exceptions for human review, turning time-consuming checks into targeted interventions.
Energy and safety. AI flattens power peaks by scheduling charging and HVAC intelligently; it also monitors near-miss patterns, adjusting traffic lanes and speed rules before incidents occur.
The goal is not a “dark” warehouse; it is a safer, more productive workplace where people handle judgement calls and customer nuance while machines handle drudge work.
Borders that think: AI and the next generation of customs
No matter how elegant your plan, your goods must still clear the border. AI helps traders and brokers submit cleaner data, anticipate risk, and reduce interventions.
Document intelligence. Models read invoices, packing lists, and certificates, propose HS codes, validate values and currencies, and detect missing licences. That means fewer last-minute scrambles and lower rejection rates.
Rules-of-origin and preference. AI checks bill-of-materials and supplier statements to estimate preferential eligibility and warn when content thresholds may be missed. Planning teams can then adjust sourcing or processing to preserve tariff benefits.
Safety and security filings. Pre-departure ENS declarations benefit from AI that verifies parties, transport, and commodity data against historical anomalies before the filing is sent—shifting the work left and avoiding “orange lane” holds.
If your team needs a practical starting point, a modern platform that streamlines CDS declarations and related filings helps you standardise and validate data once and reuse it across movements. See the CDUK digital customs platform for automation options, and the CDUK Knowledge Base for primers on import declarations, export declarations, and best practices for any customs declaration. For a wider perspective on pre-arrival security data, the EU’s evolving ICS2 framework is a useful external reference for ENS declarations and risk-based targeting across EU borders.
Sustainability by design, not apology
The future supply chain must cut emissions while improving service. AI makes decarbonisation operational rather than aspirational.
Carbon-aware planning. Routing engines consider grid intensity and charge-station availability to steer electric fleets to lower-carbon energy. Mode-mix models price CO₂ explicitly alongside time and cost, elevating rail or short-sea where feasible.
Waste reduction. Better demand sensing reduces expired and obsolete stock. Computer vision flags damage early, and predictive maintenance extends asset life for forklifts, conveyors, and HGVs.
Supplier climate risk. AI scans disclosures, weather risk, and satellite data to identify suppliers vulnerable to heat, flood, or wildfire, enabling proactive dual-sourcing and resilience investments.
Data foundations: what you must get right before AI scales
AI is only as good as the data you feed it—and the governance that keeps that data trustworthy.
Master data rigour. Clean product catalogues, unit conversions, HS mappings, and partner identifiers are non-negotiable. Small inconsistencies cascade into failed bookings, mispicks, and border delays.
Event standards and APIs. Replace emailed spreadsheets with event streams: order created, goods packed, vehicle departed, container gated in, customs cleared. API-first design lets AI learn sequences and correlations in near real time.
Explainability and controls. For regulated decisions—customs classification, carrier safety, credit—use models that show their work. Confidence scores, feature importance, and human-override mechanisms build trust and meet audit expectations.
Security and privacy. Segment networks, encrypt data in transit and at rest, and apply least-privilege access. Where biometric or highly sensitive data are used (e.g., driver identity, export licences), implement explicit consent and retention policies.
A pragmatic adoption roadmap
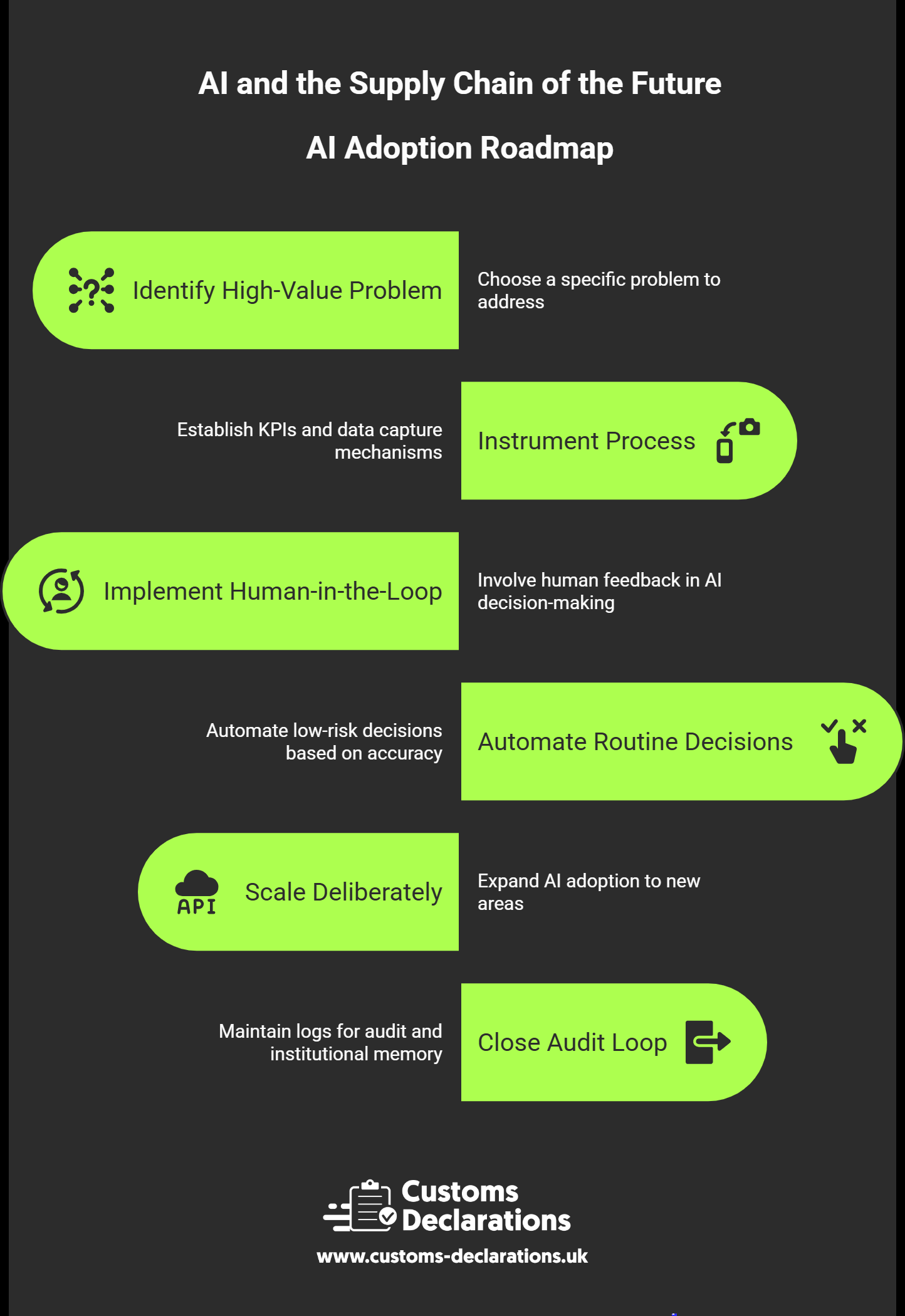
Overhauls fail; focused programs win. A sensible adoption sequence looks like this:
- Pick one high-value problem. For many operators, dynamic routing on a congested lane or AI-assisted classification for a problematic product family is the fastest way to prove ROI.
- Instrument the process. Establish baseline KPIs (on-time performance, empty miles, rework rate on declarations). Ensure you can capture the data needed to improve them.
- Start human-in-the-loop. Let planners and declarants accept, edit, or reject AI recommendations. Their feedback is training data; accuracy rises quickly when you capture it.
- Automate the “boring middle.” Once accuracy crosses a threshold, auto-approve low-risk decisions (e.g., standard lanes, well-known SKUs) and escalate only the outliers.
- Scale deliberately. Extend to adjacent sites, products, and partners. Standardise interfaces and retraining cycles so the next rollout is faster.
- Close the audit loop. Preserve immutable logs of inputs, model versions, and decisions. This cuts audit time and builds institutional memory.
Frequently asked questions
Will AI replace planners, drivers, or declarants?
AI replaces drudge work, not judgement. Planners still negotiate trade-offs and service promises; drivers still ensure safety and customer experience; declarants still carry legal accountability. The mix of tasks changes, but the need for skilled people increases.
How accurate are AI forecasts and route decisions in practice?
Accuracy depends on data quality and feedback. With clean events and captured outcomes, models quickly outperform static rules. Expect rapid gains in the first 90 days on a well-scoped pilot, then steady improvement as feedback compounds.
What is the payback period for warehouse AI and robotics?
Software-only use cases (slotting, tasking, vision QA) often pay back within 6–12 months. Hardware automation timelines vary by scale, but AI-guided changes to process and layout typically deliver benefits within one peak season.
Can AI really reduce customs delays?
Yes—by eliminating the causes of delay: missing data, misclassification, valuation errors, and untimely safety and security filings. Clean, validated data and pre-lodged filings get fewer interventions and faster releases.
What if my systems are old and disconnected?
You do not need a rip-and-replace. Introduce a lightweight integration layer to expose data through modern APIs, and pilot AI around the edges first. As value builds, upgrade core systems with less risk.
How do we ensure AI decisions are compliant and auditable?
Choose tools that store model versions, inputs, outputs, confidence scores, and human overrides. For border-relevant processes, keep human review on edge cases and align with published schema updates for filings.
The big picture: continuously learning, continuously compliant
The future supply chain is an always-on control loop: sense, decide, act, learn. AI makes it possible to operate at that cadence across planning, execution, and compliance—delivering faster cycles, lower cost, higher resilience, and demonstrably lower emissions. But it is not a silver bullet. Success depends on the quality of your master data, the discipline of your processes, and the fluency of your people.
Start by instrumenting one lane, one warehouse zone, or one product family. Use AI to eliminate friction you feel every day. Standardise and scale. And do not neglect the border: intelligent operations only deliver value if your goods clear without drama. Modern platforms that automate CDS declarations (import declarations / export declarations), and ENS declarations—backed by clear guidance and reliable integrations—are the connective tissue between your AI ambitions and real-world results.